IELTS Online
Giải đề A Chronicle of Timekeeping: IELTS Reading Cambridge 8
Mục lục [Ẩn]
Bài viết này, Langmaster sẽ hướng dẫn bạn giải trọn vẹn đề thi thật IELTS Reading “A Chronicle of Timekeeping” với đầy đủ đề bài, câu hỏi, đáp án chi tiết kèm giải thích rõ ràng. Đây sẽ là tài liệu hữu ích để bạn ôn luyện và nâng cao kỹ năng Reading, sẵn sàng chinh phục band điểm mục tiêu trong kỳ thi IELTS.
1. Đề IELTS Reading Cambridge 8: A Chronicle of Timekeeping
A Chronicle of Timekeeping
A. Before the Roman Empire even existed, at least 5,000 years ago, according to archaeological evidence, the Babylonians invented calendars to coordinate social activities, arrange the transportation of products, and, in particular, to control planting and harvesting. Their calendars were based on three natural cycles: the solar day, which corresponds to the alternation of periods of light and darkness as the earth rotates on its axis; the lunar month, which tracks the phases of the moon as it orbits the earth; and the solar year, which is determined by the varying seasons that coincide with our planet’s rotation around the sun.
B. The moon had a bigger social impact before the development of artificial light. And its growing and fading was more obvious to people who lived close to the equator than the change of the seasons. As a result, the moon cycle rather than the solar year had a greater impact on the calendars that were created in lower latitudes. The solar year, however, became more important in northern climates where seasonal agriculture was practised. The solar year served as the primary organising principle for the Roman Empire’s activity chart as it grew northward.
C. Egyptians developed a municipal calendar with 12 months of 30 days and five extra days to resemble the solar year centuries before the Roman Empire. Decans, distinctive constellations of stars, appeared every ten days to indicate a ten-day period. 12 decans may be seen sweeping the heavens at the rising of the star Sirius immediately before daybreak, which took place around the crucial yearly flooding of the Nile. The Egyptians developed a system in which each interval of darkness (and later, each interval of daylight) was divided into a dozen equal pieces due to the cosmic significance they attached to the 12 decans. These intervals, which varied in length in accordance with the length of the days and nights as the seasons changed, came to be known as temporal hours. Only at the spring and fall equinoxes were the lengths of daylight and nighttime equal. Summer hours were long, winter hours were short. Temporal hours were used for more than 2,500 years after being initially accepted by the Greeks and later the Romans, who spread them throughout Europe.
D. Sundials, which tell the time by the length or direction of the sun’s shadow, were invented by inventors to keep track of the temporal hours throughout the day. The water clock, the sundial’s inverse, was made to count the hours of the night. One of the original water clocks consisted of a basin with a tiny hole towards the bottom through which water leaked. As the water level dropped below the hour lines etched on the inner surface, it indicated the passing hour. Although these gadgets worked well around the Mediterranean, it was difficult to rely on them in northern Europe’s overcast, frequently chilly weather.
E. When the mechanical clock was invented, it was ideally suited to retaining equal hours even though it could be changed to preserve temporal ones. However, the issue of when to start counting arose with them, leading to the development of other systems in the early 14th century. Depending on the time of the count, different systems were used to divide the day into 24 equal parts: Italian time started at dusk, Babylonian time at dawn, astronomical time at noon, and the “big clock” time, which is used for some very large public clocks in Germany, at midnight. These eventually gave way to “little clock” or French hours, which divided the day into two 12-hour blocks beginning at midnight.
F. In Bedfordshire, England, a weight-driven mechanical clock was constructed in 1283. Its escapement, which had been around for at least 1,300 years, was what made this new timepiece remarkable, not the descending weight that produced its driving force or the gear wheels that conveyed the power. The coiled spring, also known as a fusee, was created in the early 1400s and kept the gear wheels of a timekeeper turning steadily despite changes in the mainspring’s tension. A pendulum clock was invented in the 16th century, but it was ineffective since the pendulum swung in a wide arc.
G. In order to solve this, an alternative to the original escapement was created in England in 1670. It was a lever-driven tool with the shape of an anchor for a ship and was known as the anchor escapement. This apparatus is rocked by a pendulum such that each escape wheel tooth is caught and then released, allowing the escape wheel to turn precisely. The anchor escapement allowed the pendulum to swing in a far smaller arc than the original design found in early pendulum clocks. Additionally, this innovation made it possible to utilise a long pendulum that could beat once per second, which encouraged the creation of a new floor-standing case style that came to be known as the grandfather clock.
H. Today, the majority of electronic devices are timed by extremely precise clocks. A quartz-crystal clock is almost always present in computers to control their operation. Furthermore, time signals transmitted by GPS satellites calibrate the operations of high-precision navigational equipment as well as mobile phones, real-time stock trading platforms, and national power grids. These time-based devices have gotten so ingrained in daily life that we only realize how dependent we are on them when they stop functioning.
Questions 1-4
Reading Passage 1 has eight paragraphs, A-H.
Which paragraph contains the following information?
Write the correct letter, A-H, in boxes 1-4 on your answer sheet.
- 1. a description of an early timekeeping invention affected by cold temperatures
- 2. an explanation of the importance of geography in the development of the calendar in farming communities
- 3. a description of the origins of the pendulum clock
- 4. details of the simultaneous efforts of different societies to calculate time using uniform hours
Questions 5-8
Look at the following events (Questions 5-8) and the list of nationalities below.
Match each event with the correct nationality, A-F.
Write the correct letter, A-F, in boxes 5-8 on your answer sheet.
5. They devised a civil calendar in which the months were equal in length.
6. They divided the day into two equal halves.
7. They developed a new cabinet shape for a type of timekeeper.
8. They created a calendar to organize public events and work schedules.
List of Nationalities
-
Babylonians
-
Egyptians
-
Greeks
-
English
-
Germans
-
French
Questions 9-13
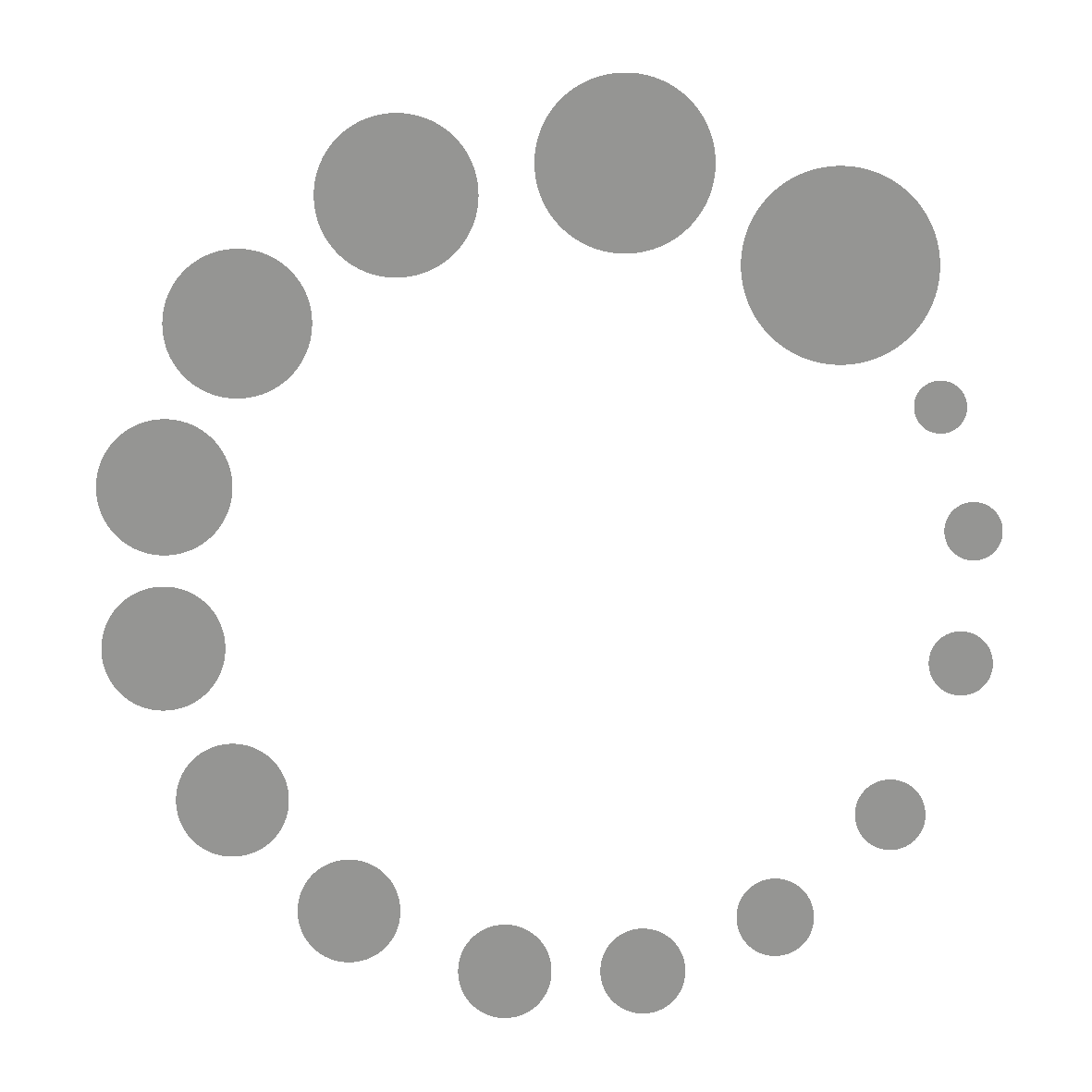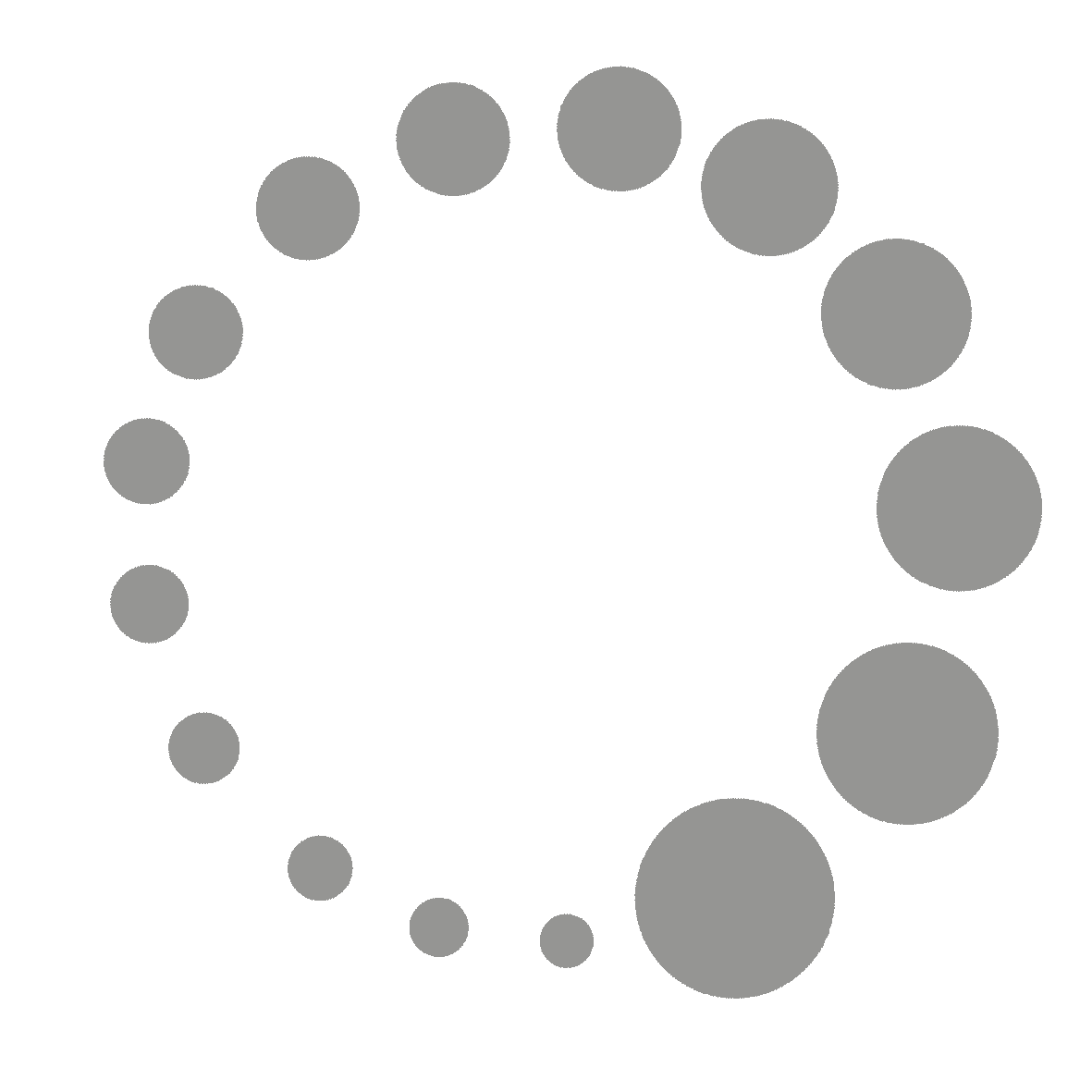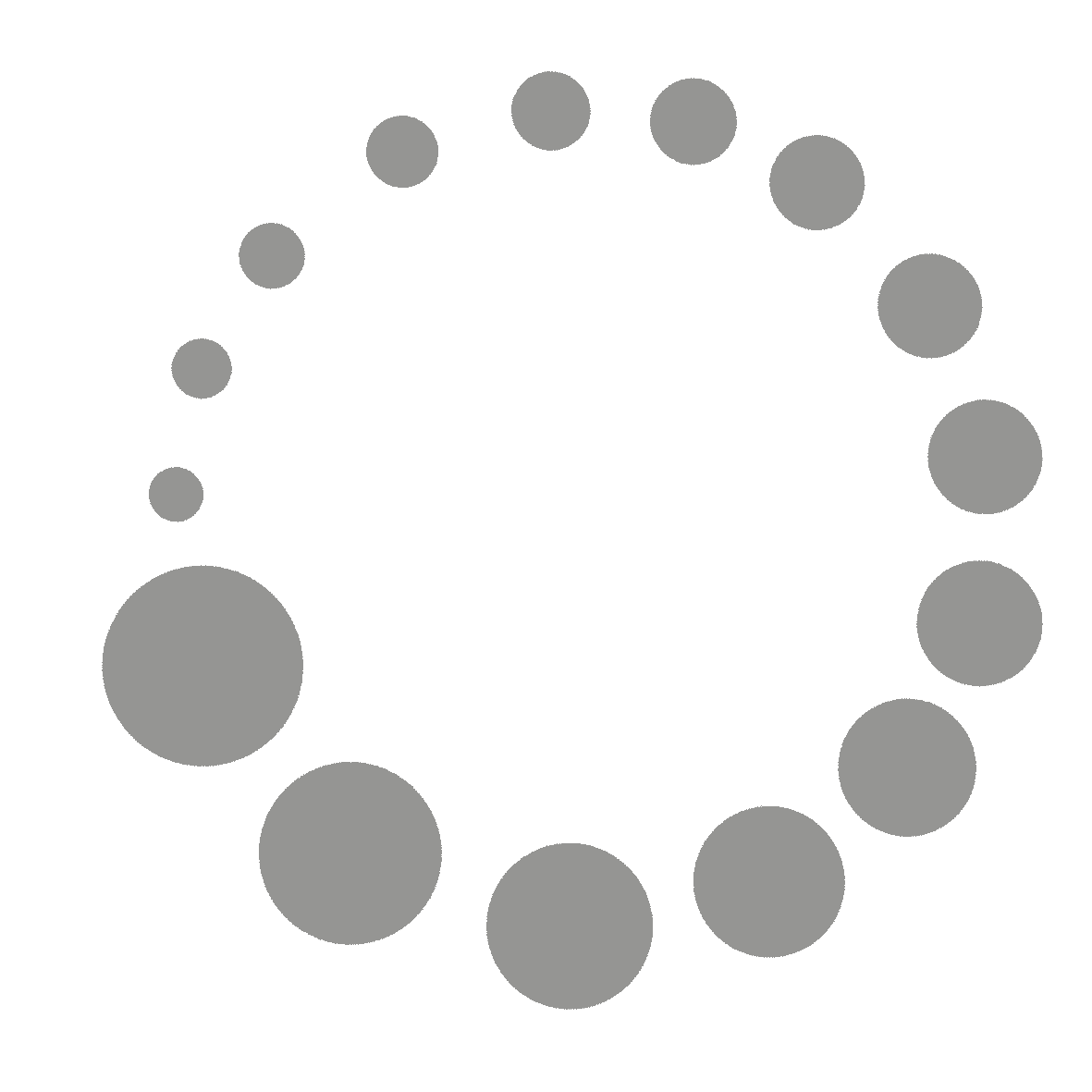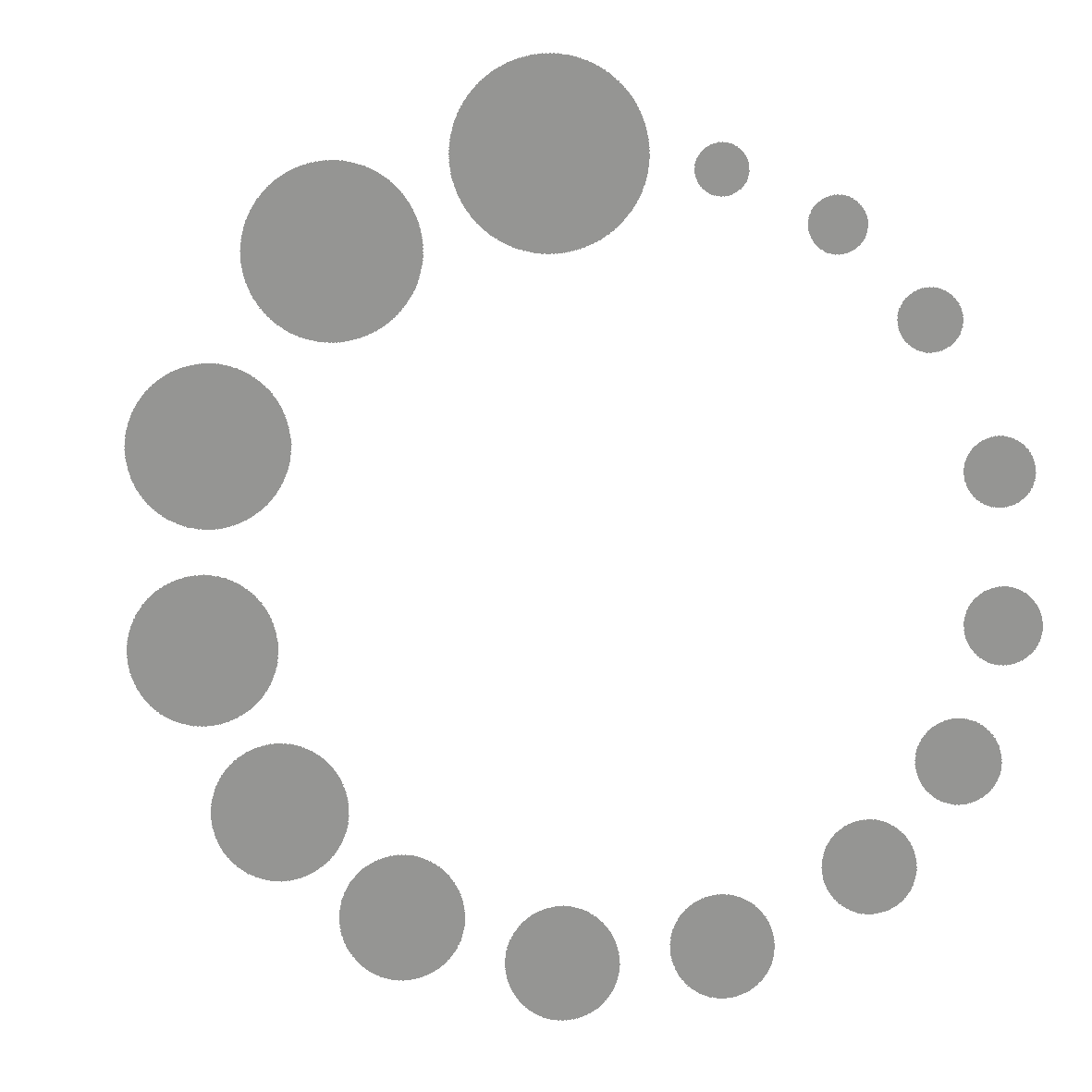
Label the diagram below.
Choose NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS from the passage for each answer.
Write your answers in boxes 9-13 on your answer sheet.
How the 1670 lever-based device worked
- escapement (resembling 9 …………………….)
- the 10 …………………….
- the 11 …………………….
- a 12 ……………………. which beats each 13 …………………….
2. Giải đề IELTS Reading Cambridge 8: A Chronicle of Timekeeping
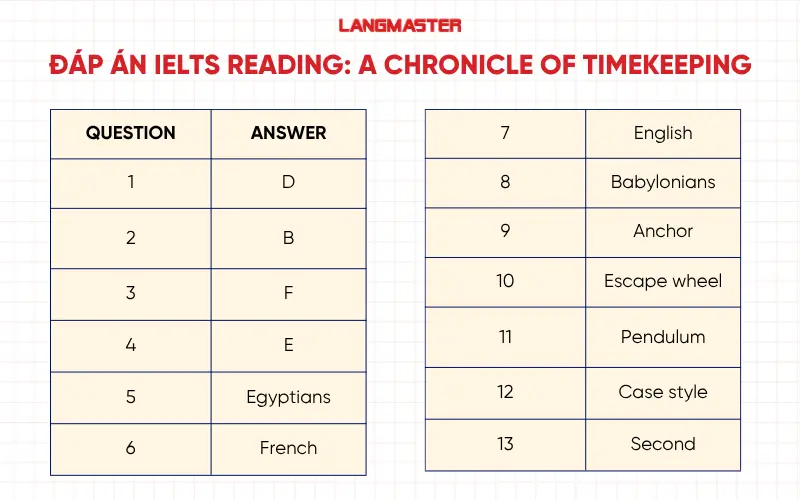
Questions 1-4
1. a description of an early timekeeping invention affected by cold temperatures
Thông tin đoạn D: “Although these gadgets worked well around the Mediterranean, it was difficult to rely on them in northern Europe’s overcast, frequently chilly weather.”
→ Ở đoạn D nói về sundials (đồng hồ mặt trời) và water clocks (đồng hồ nước). Cả hai loại này hoạt động dựa vào ánh sáng mặt trời hoặc dòng nước, nên khi thời tiết ở vùng Bắc Âu lạnh và nhiều mây, chúng không chính xác hoặc không hoạt động tốt.
“affected by cold temperatures” = “difficult to rely on … in chilly weather”
=> Đáp án: D
2. an explanation of the importance of geography in the development of the calendar in farming communities
Thông tin đoạn B: “As a result, the moon cycle rather than the solar year had a greater impact on the calendars that were created in lower latitudes. The solar year, however, became more important in northern climates where seasonal agriculture was practised.”
Giải thích:
- “geography” → nhắc đến lower latitudes và northern climates (vị trí địa lý khác nhau).
- “farming communities” → “seasonal agriculture was practised.”
- Đoạn này giải thích rằng ở vùng nhiệt đới (gần xích đạo) người ta dựa vào chu kỳ mặt trăng, còn ở vùng ôn đới có nông nghiệp theo mùa thì dựa vào năm mặt trời (solar year).
=> Đáp án: B
3. a description of the origins of the pendulum clock
Thông tin đoạn F: (F) “A pendulum clock was invented in the 16th century, but it was ineffective since the pendulum swung in a wide arc.”
Giải thích:
- “origins” → nguồn gốc, sự ra đời.
- Đoạn F nói rõ khi nào (thế kỷ 16) và vấn đề ban đầu của chiếc đồng hồ quả lắc (pendulum clock).
- Đây chính là mô tả nguồn gốc loại đồng hồ này.
=> Đáp án: F
4. details of the simultaneous efforts of different societies to calculate time using uniform hours
Thông tin đoạn E: “Depending on the time of the count, different systems were used to divide the day into 24 equal parts: Italian time started at dusk, Babylonian time at dawn, astronomical time at noon, and … at midnight.”
Giải thích:
- “different societies” → Italian, Babylonian, astronomical, German systems.
- “uniform hours” → “24 equal parts”.
- Đoạn E mô tả nhiều hệ thống khác nhau cùng chia 1 ngày thành 24 giờ bằng nhau, chỉ khác về thời điểm bắt đầu đếm giờ.
=> Đáp án: E
Questions 5-8
5. They devised a civil calendar in which the months were equal in length.
Thông tin đoạn C: “Egyptians developed a municipal calendar with 12 months of 30 days and five extra days to resemble the solar year...”
Giải thích:
- “municipal calendar” = “civil calendar” (lịch dân sự).
- Mỗi tháng có 30 ngày bằng nhau → đúng mô tả.
=> Đáp án: B – Egyptians
6. They divided the day into two equal halves.
Thông tin đoạn E: “…‘little clock’ or French hours, which divided the day into two 12-hour blocks beginning at midnight.”
Giải thích:
- “two 12-hour blocks” = chia ngày thành hai phần bằng nhau (12h + 12h).
- Được gọi là “French hours” → quốc tịch French.
=> Đáp án: F – French
7. They developed a new cabinet shape for a type of timekeeper.
Thông tin đoạn G: “...this innovation made it possible to utilise a long pendulum ... which encouraged the creation of a new floor-standing case style that came to be known as the grandfather clock.”
Giải thích:
- “floor-standing case style” = kiểu tủ đứng (cabinet shape).
- “grandfather clock” có nguồn gốc ở England.
- Đoạn G nói rõ đây là phát minh ở England (In order to solve this ... was created in England in 1670).
=> Đáp án: D – English
8. They created a calendar to organize public events and work schedules.
Thông tin đoạn A: “The Babylonians invented calendars to coordinate social activities, arrange the transportation of products, and, in particular, to control planting and harvesting.”
Giải thích:
- “coordinate social activities” = tổ chức sự kiện xã hội.
- “arrange the transportation of products” = sắp xếp công việc, sản xuất.
→ Đúng mô tả.
=> Đáp án: A – Babylonians
Questions 9-13
Thông tin đoạn G: “In order to solve this, an alternative to the original escapement was created in England in 1670. It was a lever-driven tool with the shape of an anchor for a ship and was known as the anchor escapement. This apparatus is rocked by a pendulum such that each escape wheel tooth is caught and then released, allowing the escape wheel to turn precisely. The anchor escapement allowed the pendulum to swing in a far smaller arc than the original design found in early pendulum clocks. Additionally, this innovation made it possible to utilise a long pendulum that could beat once per second...”
- escapement (resembling 9 …………………….)
- the 10 …………………….
- the 11 …………………….
- a 12 ……………………. which beats each 13 …………………….
9. anchor
10. escape wheel
11. pendulum
12. case style (nếu hình minh họa là chiếc tủ đồng hồ – tức “grandfather clock” → case cũng chấp nhận, nhưng theo đề dạng “label the diagram”, đúng nhất là “case style”)
13. second
3. Từ vựng IELTS Reading Cambridge 8: A Chronicle of Timekeeping
Dưới đây là tổng hợp những từ vựng quan trọng trong bài History of Timekeeping, bao gồm các thuật ngữ học thuật, từ chuyên về lịch sử và khoa học, cùng với nghĩa tiếng Việt giúp bạn dễ hiểu và ghi nhớ hơn khi ôn luyện IELTS Reading.
- archaeological evidence (n) – bằng chứng khảo cổ
- coordinate (v) – phối hợp, sắp xếp
- social activities (n) – hoạt động xã hội
- transportation of products (n) – việc vận chuyển hàng hóa
- solar day (n) – ngày mặt trời
- lunar month (n) – tháng mặt trăng
- solar year (n) – năm mặt trời
- sundial (n) – đồng hồ mặt trời
- water clock (n) – đồng hồ nước
- etch (v) – khắc, chạm khắc
- overcast (adj) – u ám (thời tiết)
- chilly (adj) – lạnh giá, se lạnh
- mechanical clock (n) – đồng hồ cơ học
- divide into equal parts (v) – chia thành các phần bằng nhau
- Italian time / French hours (n) – hệ thống giờ kiểu Ý / Pháp
- dusk (n) – hoàng hôn
- dawn (n) – bình minh
- escape wheel (n) – bánh răng thoát
- pendulum (n) – con lắc
- case style / floor-standing case (n) – kiểu tủ đứng (vỏ đồng hồ)
- grandfather clock (n) – đồng hồ quả lắc lớn (đồng hồ tủ)
- beat once per second (v) – dao động mỗi giây
Khi luyện tập với các đề thi mẫu như đề IELTS Reading “A Chronicle of Timekeeping”, chắc hẳn bạn sẽ có nhiều câu hỏi cần giải đáp về logic làm bài cũng như cách học từ vựng hiệu quả hơn. Để làm được điều đó, bạn có thể tìm một lộ trình học bài bản và một giáo viên giàu kinh nghiệm để giúp bạn tiến bộ nhanh trong việc luyện thi IELTS.
Với hơn 16 năm kinh nghiệm giảng dạy tiếng Anh, Langmaster mang đến các khóa học IELTS online được thiết kế phù hợp với từng mục tiêu và năng lực đầu vào của học viên. Chính những ưu điểm nổi bật dưới đây đã giúp khóa học của Langmaster trở thành lựa chọn đáng tin cậy cho những ai muốn chinh phục IELTS một cách bền vững:
- Sĩ số lớp nhỏ (7 - 10 học viên): Giúp mỗi học viên có nhiều cơ hội trao đổi trực tiếp với giảng viên, được chữa bài chi tiết và tiến bộ đồng đều.
- Lộ trình cá nhân hóa: Được xây dựng dựa trên bài đánh giá năng lực đầu vào và có báo cáo tiến độ hàng tháng, đảm bảo việc học tập đúng hướng.
- Giáo viên 7.5+ IELTS: Có chuyên môn cao và cam kết chấm chữa bài cho học viên trong vòng 24h, đồng hành sát sao để học viên sửa lỗi nhanh chóng.
- Thi thử chuẩn thi thật: Giúp làm quen áp lực phòng thi, đồng thời phân tích rõ điểm mạnh - yếu của học viên để cải thiện hơn.
- Cam kết đầu ra: Khóa học cam kết giúp bạn đạt band điểm mục tiêu, hỗ trợ học lại miễn phí nếu khi thi chưa đạt band.
- Học online linh hoạt: Lịch học dễ sắp xếp, có ghi hình lại buổi học và coaching 1-1 để ôn tập chuyên sâu.
- Hệ sinh thái đồng hành: Kho tài liệu phong phú, bài tập trực tuyến và cố vấn học tập theo sát từng bước.
Đặc biệt, bạn còn có thể tham gia lớp học thử miễn phí tại Langmaster, trực tiếp trải nghiệm phương pháp giảng dạy và đánh giá mức độ phù hợp của khóa học trước khi quyết định đăng ký chính thức với trung tâm.
Trên đây là toàn bộ đáp án đề thi IELTS Reading “A Chronicle of Timekeeping” kèm giải thích chi tiết và từ vựng quan trọng. Khi luyện tập theo đề thi thật, bạn không chỉ nắm chắc cách làm dạng bài mà còn mở rộng vốn từ học thuật hữu ích cho kỳ thi. Hy vọng tài liệu này sẽ giúp bạn tự tin hơn, cải thiện kỹ năng đọc hiểu và tiến gần hơn tới band điểm IELTS mục tiêu.
Nội Dung Hot
KHÓA TIẾNG ANH GIAO TIẾP 1 KÈM 1
- Học và trao đổi trực tiếp 1 thầy 1 trò.
- Giao tiếp liên tục, sửa lỗi kịp thời, bù đắp lỗ hổng ngay lập tức.
- Lộ trình học được thiết kế riêng cho từng học viên.
- Dựa trên mục tiêu, đặc thù từng ngành việc của học viên.
- Học mọi lúc mọi nơi, thời gian linh hoạt.

KHÓA HỌC IELTS ONLINE
- Sĩ số lớp nhỏ (7-10 học viên), đảm bảo học viên được quan tâm đồng đều, sát sao.
- Giáo viên 7.5+ IELTS, chấm chữa bài trong vòng 24h.
- Lộ trình cá nhân hóa, coaching 1-1 cùng chuyên gia.
- Thi thử chuẩn thi thật, phân tích điểm mạnh - yếu rõ ràng.
- Cam kết đầu ra, học lại miễn phí.

KHÓA TIẾNG ANH TRẺ EM
- Giáo trình Cambridge kết hợp với Sách giáo khoa của Bộ GD&ĐT hiện hành
- 100% giáo viên đạt chứng chỉ quốc tế IELTS 7.0+/TOEIC 900+
- X3 hiệu quả với các Phương pháp giảng dạy hiện đại
- Lộ trình học cá nhân hóa, con được quan tâm sát sao và phát triển toàn diện 4 kỹ năng
Bài viết khác

Các dạng bài phổ biến và tiêu chí chấm điểm IELTS Reading chi tiết nhất: Multiple Choice, Matching Information, Matching Headings,... và hướng dẫn chiến lược làm bài hiệu quả

Những sai lầm khi luyện IELTS Reading bao gồm: dịch từng từ, đọc hết cả bài, không đọc câu hỏi trước, không quản lý thời gian, không nắm vững kỹ năng paraphrase, viết sai chính tả
![Giải đề IELTS Reading: A brief history of humans and food [full answers]](https://langmaster.edu.vn/storage/images/2025/09/20/a-brief-history-of-humans-and-food-ielts-reading-answers.webp)
Giải đề thi IELTS Reading “A brief history of humans and food” kèm full đề thi thật, câu hỏi, đáp án, giải thích chi tiết, và từ vựng cần lưu ý khi làm bài.

Tổng hợp IELTS Reading tips hay nhất giúp bạn đọc nhanh, nắm ý chính và xử lý thông tin chính xác, tự tin đạt điểm cao trong kỳ thi IELTS.
![Giải đề IELTS Reading: The importance of law [Full answers]](https://langmaster.edu.vn/storage/images/2025/09/22/55.webp)
Giải đề IELTS Reading “The importance of law” kèm đáp án chi tiết, từ vựng quan trọng và bí quyết luyện thi hiệu quả để nâng cao band điểm.








.png)
![Giải đề IELTS Reading Actual Test Vol 6 Test 5: The Pearl [FULL ANSWER]](https://langmaster.edu.vn/storage/uploads/original/2025/10/08/the-pearl-ielts-reading.png)